Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. While there is no known cure for AS, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. In this article, we will discuss what AS is, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
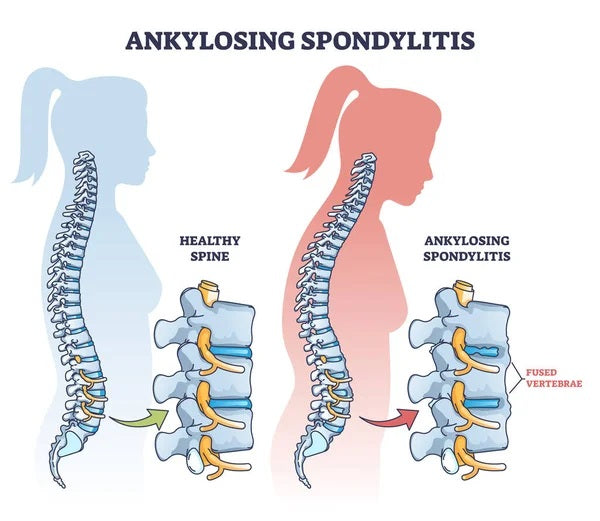
AS is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the spine, but can also affect other joints in the body. It is a type of arthritis that causes inflammation of the joints between the vertebrae, which can lead to fusion of the spine over time. This fusion can cause stiffness and immobility in the spine, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
The symptoms of AS can vary from person to person, and may develop gradually over time. The most common symptoms of AS include:
- Pain and stiffness in the lower back, hips, and buttocks that lasts for more than three months
- Pain and stiffness that worsens with rest and improves with physical activity
- Reduced flexibility in the spine
- Fatigue and lack of energy
- Loss of appetite
- Mild fever
- Inflammation of the eyes (uveitis)
Diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Diagnosing AS can be challenging because the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. A doctor will typically take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination to check for signs of inflammation and stiffness. They may also order blood tests to check for signs of inflammation and genetic testing to see if you carry the HLA-B27 gene, which is associated with AS.
In some cases, a doctor may order imaging tests such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans to check for changes in the spine and other joints.
Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
While there is no cure for AS, treatment can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Treatment options include:
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, while disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help slow the progression of the disease.
Physical therapy
Exercise and stretching can help improve flexibility and reduce pain and stiffness.
Biologic therapy
Biologic drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, can help reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be required to replace damaged joints or correct spinal deformities.
Prevention of Ankylosing Spondylitis
While there is no known way to prevent AS, there are several things you can do to help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease:
Maintain good posture
Good posture can help reduce the strain on your spine and reduce the risk of developing spinal deformities.
Exercise regularly
Engaging in regular exercise and stretching is pivotal for managing AS. These activities enhance flexibility, alleviate pain and stiffness, and contribute to the overall well-being of joints affected by AS. By focusing on maintaining proper posture, preserving joint function, and preventing spinal fusion, exercise becomes a crucial element in slowing down the progression of the disease. Additionally, it positively impacts mental health by alleviating stress and promoting a sense of community through social engagement in group exercises. An individualized exercise plan, developed with healthcare professionals, ensures safety and effectiveness, with regular monitoring allowing for necessary adjustments based on the individual's condition and disease progression. Overall, exercise emerges as a multifaceted approach that not only addresses physical symptoms but also supports mental and emotional well-being in individuals dealing with AS.
Stop smoking
Smoking has been linked to the worsening of symptoms in individuals with AS and increase the risk of developing other health problems.
Inflammatory Response
Ankylosing Spondylitis is characterized by inflammation in the joints of the spine, which can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Smoking exacerbates inflammation in the body, intensifying the symptoms associated with AS.
Impact on Immune System
Smoking weakens the immune system, making it less effective in managing the inflammatory processes. This compromised immune response can contribute to the progression of Ankylosing Spondylitis and increase the severity of symptoms.
Reduced Treatment Efficacy
Smoking has been shown to reduce the effectiveness of certain medications used to manage Ankylosing Spondylitis. This means that individuals who smoke may experience less relief from their symptoms compared to non-smokers, even when undergoing treatment.
Joint Damage
Ankylosing Spondylitis can cause structural damage to the spine and other joints. Smoking has been associated with increased joint damage, leading to more severe and irreversible consequences in individuals with AS.
Increased Cardiovascular Risk
AS is not only confined to the spine; it can also affect other organs, including the heart. Smoking further elevates the risk of cardiovascular problems, which can be a significant concern for individuals with AS who may already face an increased risk of heart-related issues.
Pain Perception
Smoking has been linked to changes in pain perception. Individuals who smoke may experience higher levels of pain and discomfort, which can be especially problematic for those already dealing with the chronic pain associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis.
General Health Risks
Smoking is a known risk factor for various health issues, including respiratory problems, cancers, and cardiovascular diseases. For someone with Ankylosing Spondylitis, the added burden of these health risks can further compromise overall well-being.
Impact on Exercise Tolerance
Physical activity and exercise are crucial components of managing Ankylosing Spondylitis. Smoking can impair lung function and reduce exercise tolerance, making it more challenging for individuals to engage in the recommended physical activities that help alleviate AS symptoms.
In summary, smoking not only exacerbates the symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis but also poses additional risks to the overall health of individuals with this condition. Quitting smoking is a crucial step in managing AS effectively and improving long-term outcomes.
Manage stress
Stress can worsen symptoms of AS, so it's important to find ways to manage stress, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
It's important to note that AS can also have an impact on mental health. Chronic pain, fatigue, and limited mobility can take a toll on emotional well-being. It's important to talk to your doctor if you are experiencing symptoms of depression, anxiety, or other mental health concerns. They may be able to refer you to a mental health professional who can help.
Additionally, joining a support group or talking to others who have AS can also be helpful. This can provide a sense of community and help individuals feel less alone in their struggles with the disease.
In conclusion
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that can have a significant impact on daily life. However, with early diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can manage symptoms and improve their quality of life. It's important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that works for you. Remember, you are not alone in your struggles with AS, and there are resources available to help you navigate this journey.
OrthoRelieve carries a range of back braces that can help relieve back pain caused by various conditions, including ankylosing spondylitis. Check them out here:
https://orthorelieve.com/collections/back-pain-relief
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.